Mechanism of action & pharmacodynamics
Nevolat® is a chemically synthesised glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA)

Nevolat® is a chemically synthesised glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA)
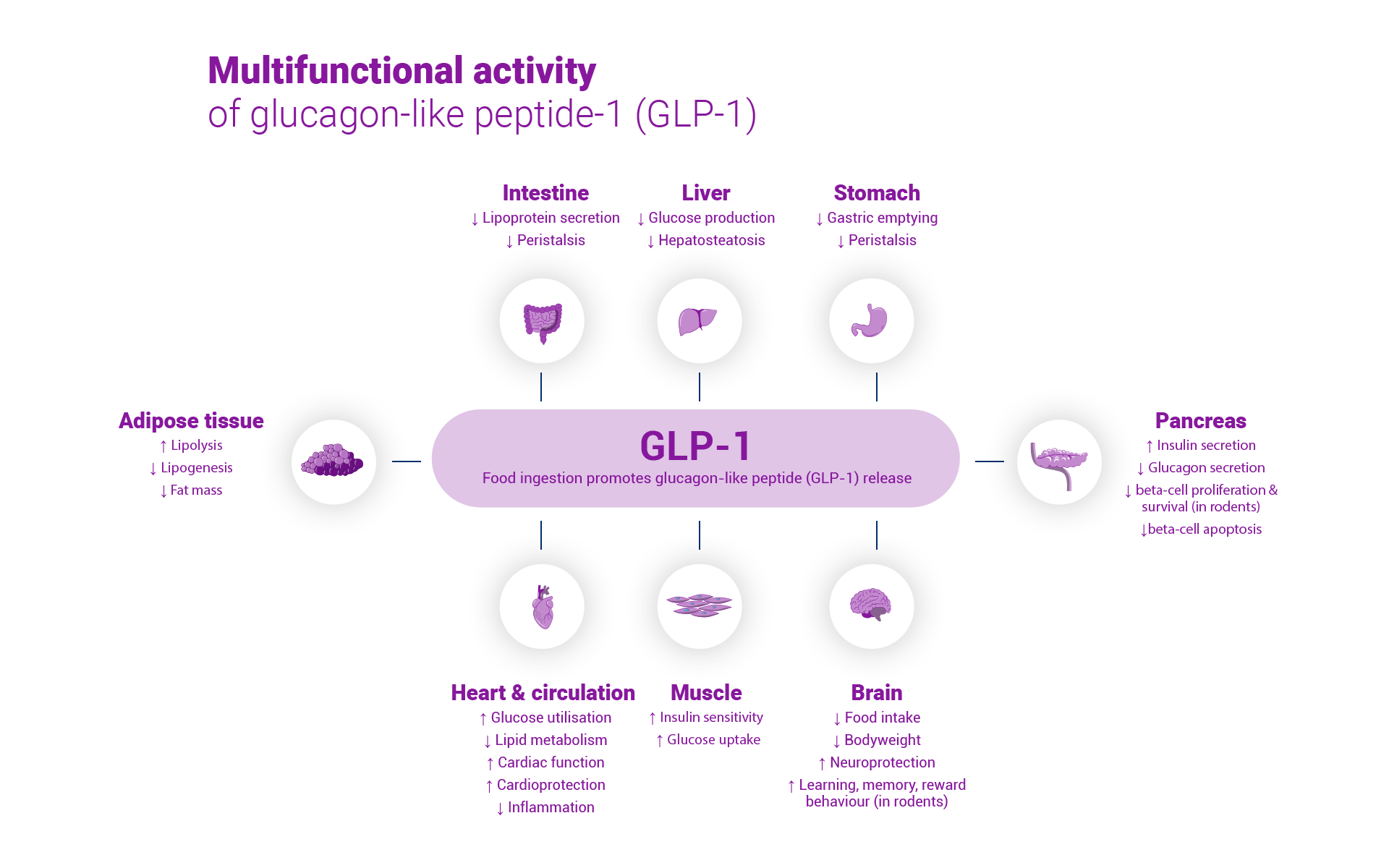
Nevolat® is a chemcially synthesised glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) with 97% sequence homology to human GLP-1 that binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor. The GLP-1 receptor is the target for native GLP-1, an endogenous incretin hormone that amplifies glucose-dependent insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells and acts as a physiological regulator of appetite and food intake. Although the exact mechanism of action is not entirely clear. In animal studies, peripheral administration of liraglutide led to uptake in specific brain regions involved in regulation of appetite. Via specific activation of the GLP-1R, liraglutide increased key satiety and decreased key hunger signals, thereby leading to a reduction in body weight.
GLP-1 receptors are also expressed in specific locations in the heart, vasculature, immune system, and kidneys. In murine models of atherosclerosis, liraglutide prevented aortic plaque progression and reduced plaque inflammation and demonstrated a beneficial effect on plasma lipids.1
Pharmacodynamic effects
Liraglutide lowers body weight in humans mainly through loss of fat mass with relative reductions in visceral fat being greater than for subcutaneous fat loss. Liraglutide regulates appetite by increasing feelings of fullness and satiety, while lowering feelings of hunger and prospective food consumption, thereby leading to reduced food intake. Liraglutide does not increase energy expenditure compared to placebo. Liraglutide stimulates insulin secretion and lowers glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner which results in a lowering of fasting and postprandial glucose. The glucose-lowering effect is more pronounced in patients with pre-diabetes and diabetes compared to patients with normoglycaemia. Clinical trials suggest that liraglutide improves and sustains beta-cell function, according to HOMA-B and the proinsulin-to-insulin ratio.1

What does this mean for your patients?
Appetite suppression and increased satiety
Nevolat® targets native GLP-1 to amplify glucose-dependent insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells and acts as a physiological regulator of appetite and food intake.1
Reduced bodyweight (visceral fat loss and subcutaneous fat loss)
In the SCALE Obesity & Pre-Diabetes trial a total of 3,731 patients with obesity (BMI ≥30 kg/m²) or who were overweight (BMI ≥27 kg/m²) with dyslipidaemia and/or hypertension were randomly assigned patients in a 2:1 ratio to receive once-daily subcutaneous injections of liraglutide or placebo. Mean weight loss at 56 weeks was 2.8 ± 6.5 kg with placebo and 8.4 ± 7.3 kg with liraglutide. A difference of -5.6 kg; 95% confidence interval, -6.0 to -5.1; P<0.001.3
Improved glycaemic control (especially in pre-diabetic and diabetic patients)
The effect of liraglutide on glycaemic control was analysed across five double-blind, randomised, controlled clinical phase 3a trials in 3,978 adult patients.1 Liraglutide treatment produced clinically and statistically significant improvements in glycosylated haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose compared with placebo.1
Once-daily administration
Nevolat® possesses a protracted action profile based on three mechanisms: self-association, which results in slow absorption; binding to albumin; and higher enzymatic stability towards the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) and neutral endopeptidase (NEP) enzymes, resulting in a long plasma half-life.1
GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; HOMA-B, Homeostasis model of Beta-cell function.
- Nevolat® (liraglutide) Summary of Product Characteristics.
- Tan Q, Akindehin SE, Orsso CE, Waldner, RC, DiMarchi RD, Müller TD, & Haqq AM (2022). Recent Advances in Incretin-Based Pharmacotherapies for the Treatment of Obesity and Diabetes. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 13, 838410. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.838410
- Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K et al. A Randomised, Controlled Trial of 3.0 mg of Liraglutide in Weight Management. New Engl J Med 2015;373:11–22.
000697586 | December 2024